This article incorporates text in the public. If the epicondyles are visible.

Lateral Epicondyle Of The Femur Wikipedia
Facet for articulation with acromion Define Superior Medial and Lateral Close to the Close to the manubrium Scapulae S-shaped.

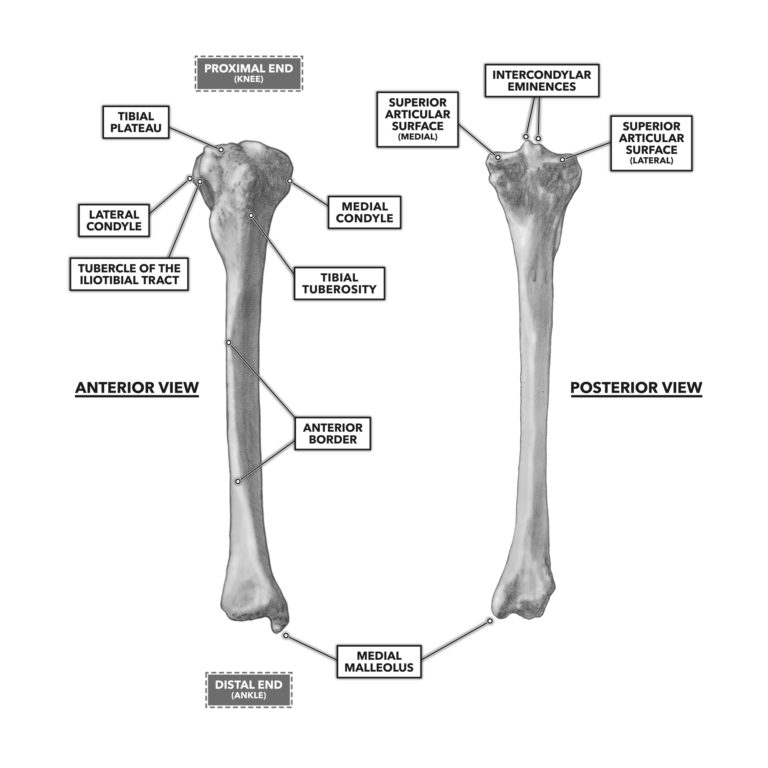
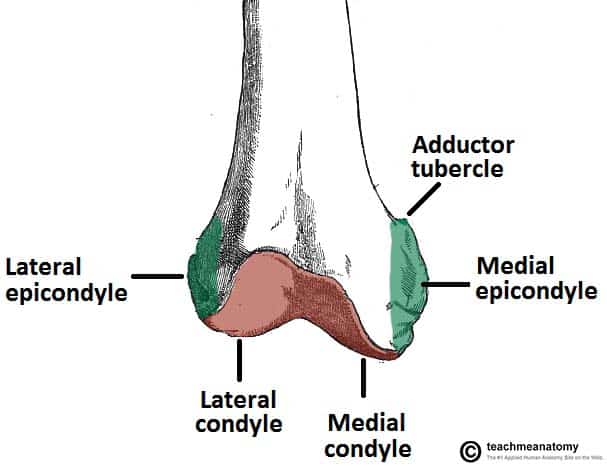
. MedialLateral Lock Do not impact Inset Only Posterior Referencing VarusValgus. The medial condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of femur the other being the lateral condyle. Lateral and medial condyles.
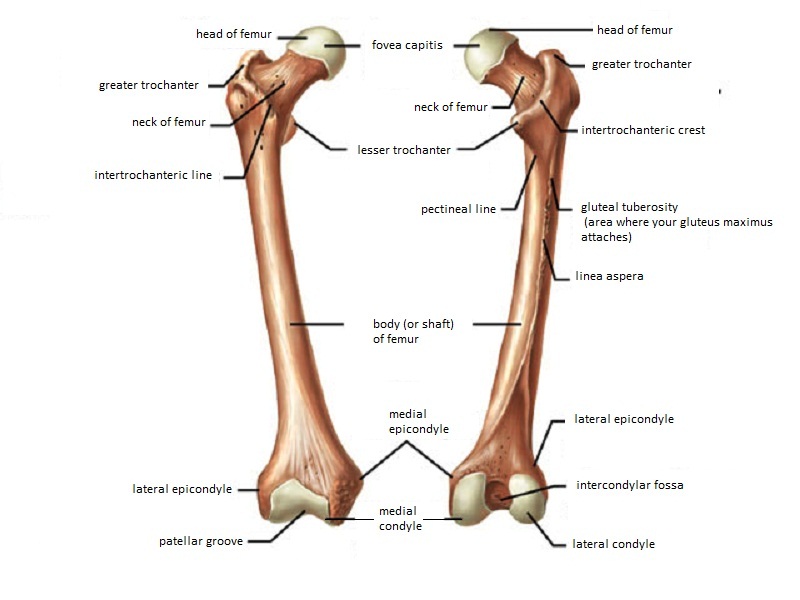
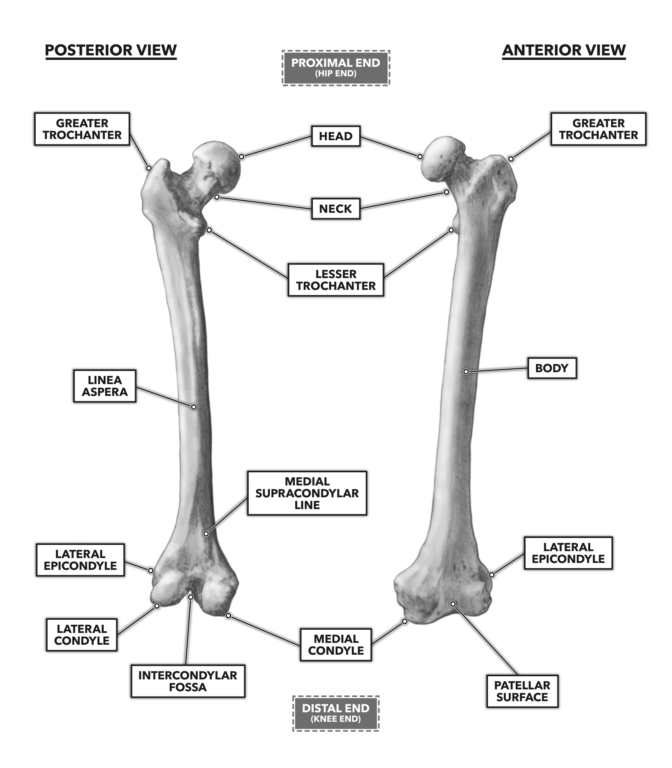
Proximal shaft and distal. In this article we shall look at the anatomy of the femur its attachments bony landmarks and clinical correlations. The femur is the only bone in the thigh and the longest bone in the body.
Femur in 3 of additional flexion to protect from notching the anterior cortex. The medial condyle is larger than the lateral outer condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the centre of mass being medial to the knee. Posteriorly these condyles are separated by the deep intercondylar fossa.
Anteriorly on the distal femur is the smooth patellar surface which forms a joint with the patella or kneecap. Distally on the femur are the lateral and medial condyles which articulate with the tibia below. Epicondyles grand trochanter trochlée pendant la flexion.
Nerf sciatique L4à S3 passe en arrière du fémur en regard de la ligne âpre et se divise en nerf fibulaire commun en dehors et nerf tibial en dedans. The human femur can resist forces of 1800 to 2500 pounds so it. The acromion protects the suprascapular nerve that lies underneath it therefore this nerve is susceptible to physical damage in pigs and horses.
The epicondyles and trochanters are all important attachment sites for various muscles. On the posterior surface of the condyle the linea aspera a ridge with two lips. It consists of 2 surfaces medial and lateral 3 borders cranial caudal and dorsal and 3 angles craniodorsal caudodorsal and ventral angle.
Once rotation is obtained the next step is to determine the depth of the Flexion Gap. It acts as the site of origin and attachment of many muscles and ligaments and can be divided into three parts. Key facts about the femur.
The lateral epicondyle of the femur smaller and less prominent than the medial epicondyle gives attachment to the fibular collateral ligament of the knee-jointDirectly below it is a small depression from which a smooth well-marked groove curves obliquely upward and backward to the posterior extremity of the condyle. Insert trocar-tipped pins through the two standard pin holes. 20212022 ICD-10-CM Index F Terms Index Terms Starting With F Fracture traumatic Index Terms Starting With F Fracture traumatic.
Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes that allow them to function in different ways. Proximal end - head neck greater trochanter lesser trochanter intertrochanteric crest Shaft - Borders. If you internally rotate the femur it causes too much bone to be taken off the lateral condyle and too little taken off the medial condyle leading to a tight medial side and loose lateral side.
LATERAL MEDIAL Acromial end Sternal end Superior view of the right clavicle. Some like the bones in our fingers are small to allow for dexterous movements. The pig and horse do not have an acromion.
Lateral ridge gluteal tuberosity pectineal line spiral line these three lines converge and form the linea aspera Distal end - lateral and medial condyles intercondylar. Malrotation also affects the flexion gap.
Femur Anatomy And Attachments Bone And Spine
Orif Lag Screw For Lateral Medial Femoral Epicondyle Fracture



0 comments
Post a Comment